While East Asia remains divided into two camps—one aligned with the U.S. and the other with China—recent developments have sparked speculation about a striking possibility: that the region’s economic giants—China, Japan, and South Korea—could set aside their long-standing rivalries to forge a new economic order. Such an alliance could emerge as a formidable force in Asia, challenging the U.S.-led global system and reshaping the balance of power.
This idea gained traction after reports from China, initially shared by a social media account affiliated with Chinese state media and later picked up by major outlets like DW, captured widespread interest. As the world focuses on Trump’s escalating tariff threats, East Asian nations—long dependent on trade with the U.S. and deeply embedded in global production and innovation networks—find themselves particularly exposed.
Despite historical tensions and political differences, Trump’s tariff war is increasingly seen as a common economic challenge. His policies, which make no distinction between allies and adversaries, aim to restore manufacturing to the U.S. or at least rebalance trade—a strategy that threatens to further slow growth in these East Asian economies.
Amid this uncertainty, diplomatic engagements among these nations have taken on greater significance. Meetings that might have once drawn routine attention are now closely scrutinized, with Chinese reports of closer cooperation between these states gaining widespread recognition.
The meeting in Seoul
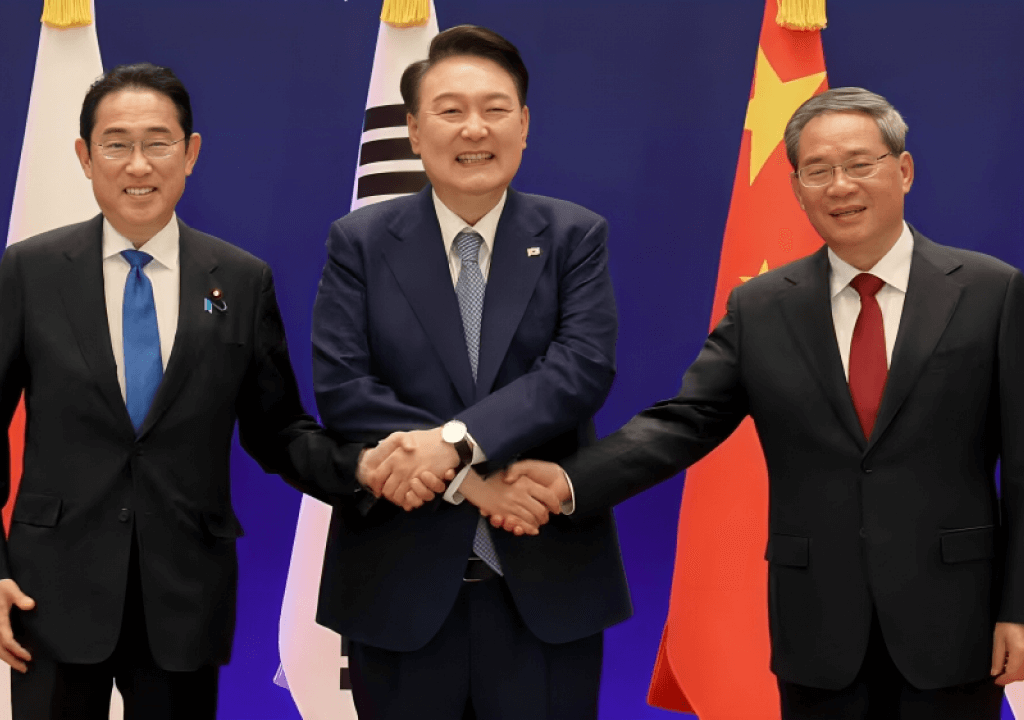
While the world was waiting for Trump’s Liberation Day announcements on new tariff rates, a pivotal meeting took place in Seoul. China, Japan, and South Korea came together to strengthen trade cooperation, bringing together South Korean Industry Minister Ahn Duk-geun, Japanese Minister of Economy, Trade, and Industry Yoji Muto, and Chinese Commerce Minister Wang Wentao.
In a joint statement released after the meeting, the three trade ministers committed to advancing comprehensive and high-level negotiations on a South Korea-Japan-China free trade agreement, aiming to bolster both regional and global trade, as reported by DW.
South Korean Trade Minister Ahn Duk-geun emphasized the need to reinforce the implementation of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), in which all three nations participate. He also highlighted the importance of creating a framework to expand trade cooperation through Korea-China-Japan FTA negotiations.
The countries further pledged to foster a stable and predictable trade and investment environment. Ahn pointed to the increasing fragmentation of the global economic landscape, stressing the necessity of collective efforts to tackle shared challenges.
As part of their ongoing collaboration, the ministers agreed to hold their next meeting in Japan.
Trump’s tariffs
As Donald Trump announced new tariffs on Wednesday, East Asia is set to bear the brunt of the economic repercussions. A base tariff of 10% has been introduced, and in a bid to rebalance trade, China, Japan, and South Korea will face even steeper taxes, with no exceptions made for U.S. allies.
Chinese imports will now be subject to a total tariff of 54%, combining a newly imposed 34% tariff with the existing 20%. Key U.S. partners have not been spared—South Korea will be hit with a 26% tariff, while Japan will face a 24% rate. The base tariffs will take effect on April 5, with the higher reciprocal rates coming into force on April 9.
Adding to the economic strain, new tariffs on automobiles and auto parts have been introduced, delivering a heavy blow to the manufacturing sectors of China, Japan, and South Korea. As home to some of the world’s largest automakers, these nations rely heavily on their automotive industries, making the new trade barriers a serious threat to their economic stability.
Obstacles outweigh potential?
While the economic benefits of closer cooperation are real, the challenges outweigh the advantages. Generational animosity between these nations remains strong, and domestic politics in each country often thrives on such rivalries. Closer collaboration could destabilize the already fragile political landscapes of Japan and South Korea, both of which face significant internal challenges. Additionally, the ideological divide between China’s communist government and Japan and South Korea’s democracies raises further concerns about compatibility.
Another major obstacle is the deep-rooted geopolitical ties—Japan and South Korea’s strong alliances with the U.S. contrast sharply with North Korea’s alignment with China. Both Tokyo and Seoul receive substantial economic and security support from Washington, and any shift toward deeper cooperation with China could put them in a difficult position. Trump, known for his retaliatory economic policies, could respond unfavorably to such a move.
Amid these complexities, a report from a social media account affiliated with Chinese state media on Monday claimed that China, Japan, and South Korea had agreed on a joint response to U.S. tariffs. However, Seoul dismissed the claim as exaggerated, and Tokyo outright denied that such discussions took place. A spokesperson for South Korea’s trade ministry stated that the assertion was overstated and pointed to the official text of the countries’ joint statement.
At a press conference on Tuesday, Japan’s Trade Minister Yoji Muto acknowledged that the trade ministers had met over the weekend but clarified that no such discussions had occurred. He described the meeting as a general exchange of views rather than a coordinated economic response. Yes, the fear is real.
What if major economies join forces?
According to the IMF, China is the world’s second-largest economy at $20 trillion, followed by Japan at $4 trillion and South Korea at $2 trillion. Together, they form a $26 trillion economy—larger than the European Union’s nominal GDP and nearing the $30 trillion U.S. economy. However, uniting these economic powerhouses remains a daunting challenge, despite their strong trade ties.
Japan and South Korea depend on China for semiconductor raw materials, while China imports advanced chip products from both nations. Acknowledging this interdependence, all three countries have pledged to strengthen supply chain cooperation and expand discussions on export controls.
At the Seoul meeting, trade ministers from China, Japan, and South Korea committed to expediting negotiations for a trilateral free trade agreement aimed at strengthening regional and global trade. A spokesperson for South Korea’s trade ministry stated that all three nations acknowledged evolving global trade dynamics and reaffirmed their dedication to ongoing economic cooperation.
Some analysts speculate about the potential formation of an Asian economic bloc that includes ASEAN and India, creating a formidable economic force. However, deep-seated rivalries, competing strategic interests, and the ambitions of some leaders to establish an “Asian NATO” pose significant challenges, making full economic integration uncertain.