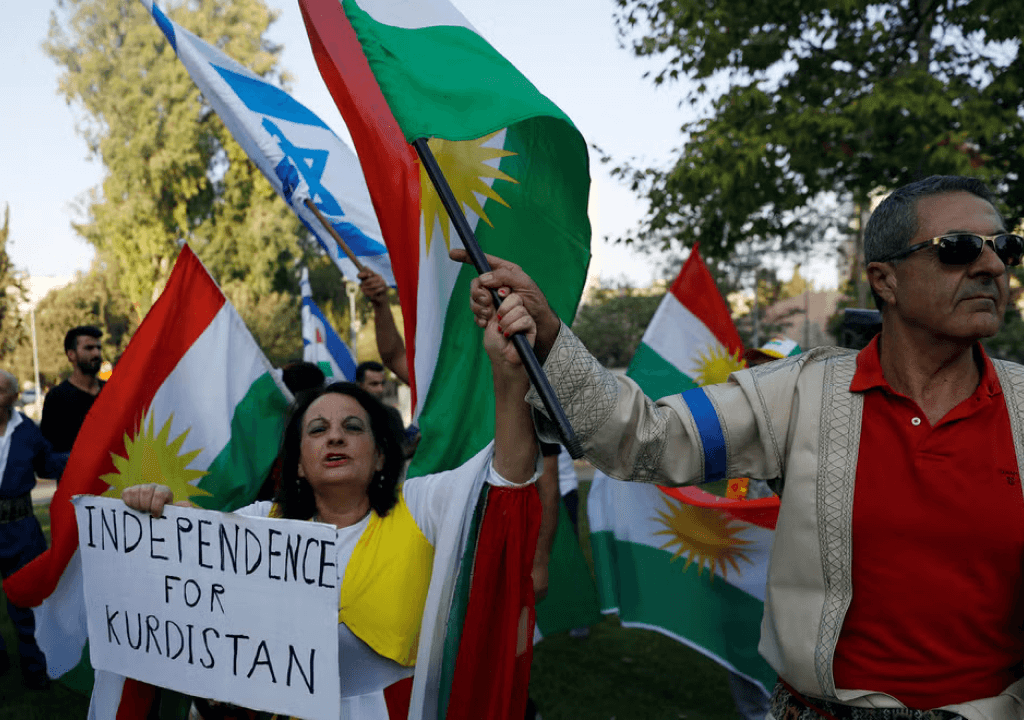
Kurdistan, the homeland of the Kurds, remains unrecognized by the world and is confronted with an unprecedented threat to its survival. The autonomous region in Iraq, having established separate administrations, military structures, and a distinct identity, is actively advocating for complete statehood but finds itself in a state of limbo.
As the United States’ closest ally in the region, with a majority Kurdish population, Kurdistan faces existential threats from neighboring countries that harbor a considerable Kurdish population antagonistic to their cause. Despite contemplating the immediate availability of statehood, the Kurds are indeed grappling with significant existential challenges. Various reasons contribute to the threats to the Kurds’ long standing aspiration for statehood, ranging from internal issues to concerns about the weakening of the American government.
The original Kurdistan, also referred to as Greater Kurdistan, is a loosely defined geo-cultural region in West Asia where Kurds constitute a significant majority population, and the foundation of Kurdish culture, languages, and national identity is deeply rooted. Geographically, Kurdistan spans the northwestern Zagros and the eastern Taurus mountain ranges.
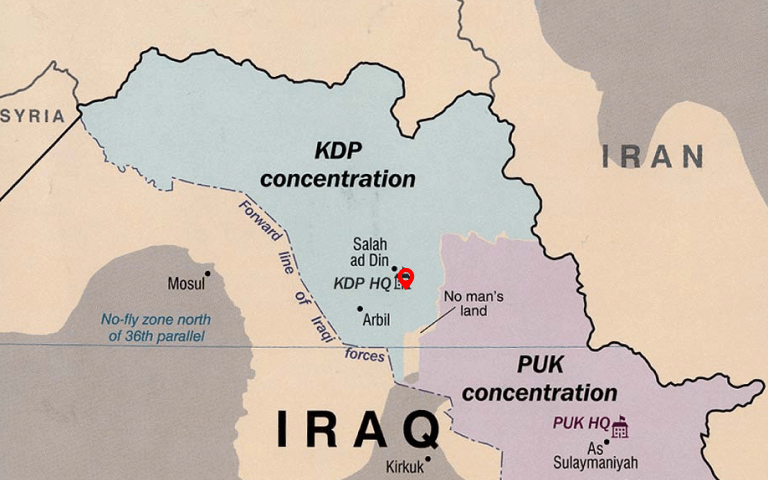
Kurdistan is commonly divided into four regions: Northern Kurdistan (southeastern Turkey), Southern Kurdistan (northern Iraq), Eastern Kurdistan (northwestern Iran), and Western Kurdistan (northern Syria). Some interpretations extend its boundaries into parts of southern Transcaucasia. Different Kurdish nationalist groups advocate for either an independent nation-state covering these regions with a Kurdish majority or increased autonomy within existing national boundaries. The precise demarcation of the region remains a contentious issue, with certain maps exaggerating its scope.
As of a 2016 estimate from the Kurdish Institute of Paris, Kurdistan’s total population is around 34.5 million, with Kurds constituting 86% of the population in Northern Kurdistan. The region also includes Arab, Turkish, Assyrian (Syriac), Armenian, and Azerbaijani minorities. Southern Kurdistan hosts Christian (Assyrian and Armenian) and Turkish (Turkmen) minorities. Kurds in Turkey, Iraq, and Iran have significant Caucasian populations that underwent Kurdification, adopting Kurdish as their primary language. Kurdish, part of the Indo-European language family except for the Semitic and Turkic languages around them, is a crucial component of Kurdish identity.
Geographically, Kurdistan covers approximately 190,000 km² in Turkey, 125,000 km² in Iran, 65,000 km² in Iraq, and 12,000 km² in Syria, totaling around 392,000 km². Turkish Kurdistan encompasses a substantial area in the Eastern Anatolia Region and southeastern Anatolia of Turkey, with an estimated 6 to 8 million Kurds residing in the region.
The term “Kurdistan” has historical origins, first documented in 11th-century Seljuk chronicles. From the 8th to the 19th centuries, a multitude of Kurdish dynasties, emirates, principalities, and chiefdoms emerged. In the 20th century, there were short-lived attempts to establish Kurdish entities, including the Kurdish state (1918–1919), Kingdom of Kurdistan (1921–1924), Red Kurdistan (1923–1929), Republic of Ararat (1927–1930), and Republic of Mahabad (1946).
Iraqi Kurdistan, which has the most chance for getting statehood and recognition from the international bodies, obtained autonomous status through a 1970 agreement with the Iraqi government, solidified as the autonomous Kurdistan Region within the federal Iraqi republic in 2005. In Iran, there is a Kurdistan Province, though it lacks self-rule. Kurds involved in the Syrian Civil War successfully seized control of significant portions of northern Syria, establishing self-governing regions under the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (commonly known as Rojava), where they aspire to achieve autonomy within a federal Syria post-war.
A 2010 report from the United States, predating the instability in Syria and Iraq as of 2014, predicted the potential existence of Kurdistan by the year 2030. The vulnerability of the Iraqi state, exacerbated by the 2014 Northern Iraq offensive by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, created an opening for Iraqi Kurdistan to pursue independence. Turkey, while historically opposing Kurdish autonomy in Turkey and Syria, shifted its stance toward acknowledging the possibility of an independent Kurdish state in Iraq.
Turkey’s long standing fear has been that a Kurdish state in Northern Iraq would fuel and support Kurdish separatists in Turkish provinces, leading to strong opposition to Kurdish independence in Iraq. However, amidst the chaos following the US invasion of Iraq, Turkey began collaborating more closely with the autonomous Kurdistan Regional Government. Despite this, the mere mention or expression of ‘Kurdistan’ in Turkey still carries the risk of detention and prosecution.
The successful 2014 Northern Iraq offensive by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant further weakened the Iraqi state’s ability to exert power, providing the Kurds with a “golden opportunity” to enhance their independence and potentially declare an independent Kurdish state. The Islamic State’s hostility towards Turkey made Kurdistan strategically valuable to Turkey as a buffer state. In June 2014, a spokesman for Turkey’s ruling Justice and Development Party expressed Turkey’s readiness to accept an independent Kurdistan in northern Iraq.
Kurdistan, endowed with abundant oil resources, has been actively engaging in economic cooperation and securing oil deals primarily with its volatile neighbor, Syria. Despite the complexities surrounding the Kurdish issue in Syria, significant oil contracts have been forged between Kurdistan and Syria. Additionally, Iran, which has recently taken a stronger stance against Kurds in the region, particularly following the Mahsini issue, has also established increased economic cooperation with Kurdistan.
According to the Iranian Free Zones News Agency (Freena), Hojatollah Abdolmaleki disclosed the collaboration during a press conference at Iran’s exclusive exhibition in Sulaymaniyah, Kurdistan region. Abdolmaleki emphasized the pivotal role of the newly established free zone in fostering cooperation between Iran and Kurdistan. The opening ceremony of the exhibition saw the participation of senior officials from both sides, including Abdolmaleki, the secretary general of the Iran-Iraq Joint Chamber of Commerce, the Iranian envoy in Sulaymaniyah, and the head of the Union of Exporters and Importers of the Kurdistan Region.
Despite several promises for statehood from the United States, Iraq, the United Nations, and occasionally from Turkey, the Kurds have faced numerous obstacles, particularly prolonged referendums driven by various reasons. Although they came close to achieving statehood in 2017, even their allies rejected the prospect. The Iraqi government has reclaimed territories once occupied by the Kurds, including areas with significant oil reserves. The collapse of oil revenues has left the Kurds grappling with serious financial challenges.
In addition to Turkey, Iran has also intensified actions against the Kurds, further contributing to the Kurds’ predicament. A significant division exists within the Kurdish population, with the ruling KDP party leaning towards Iran’s support rather than aligning with the Iraqi federal government. The United States has a vested interest in the region, providing military aid and financial assistance, with a notable presence of administrators and officials in Erbil, the capital of Kurdistan. However, the inactive governance and increased Iranian intervention have posed challenges.
Despite the current difficulties, a people with a long history of fighting for their identity and a homeland are likely to find a solution to their current problems. However, the extended decision-making process by the United States could jeopardize a key and reliable ally in the region, potentially leading to strategic consequences.








